Types of SAP BW Variables
The following types of variables can be created in SAP BW and will be discussed in detail:
- Characteristic Value Variables
- Hierarchy Node Variables
- Text Variables
- Formula Variables
- Hierarchy Variables
Characteristic Value Variables
These types of SAP BW variables act as placeholders for characteristic values. You can select not just single values for variables but also multiple single values, intervals, ranges, or selection options based on how the variable is defined. For instance, you can replace fiscal period with a variable reference:
Fiscal Period = 0062017 ➔ Fiscal Period = FISCPER_V01
Hierarchy Node Variables
If you want to select hierarchy nodes, you must use hierarchy node variables.
Text Variables
These types of variables act as placeholders for text. You can use these variables in calculated key figures, structures, and query descriptions. These variables appear as technical name surrounded by ampersands (&). For example:
Prior Year Revenue Period = 0062016 ➔ Prior Year Revenue Period = &FISCPER_T01&
Formula Variables
These types of variables represent numerical values. You can use these variables in formulas for computing conditions and exceptions.
Hierarchy Variables
These types of variables act as placeholders for hierarchies. You can use these types of variables when you want to select hierarchies.
Processing Types of SAP BW Variables
The variable processing type governs the way in which a variable gets filled with values during runtime of the query. The following are the various processing types:
- Replacement Path
- Customer Exit
- SAP Exit
- User Entry/Default Value
- Authorization
We will discuss these processing types and their valid variable types in the following sections.
Replacement Path
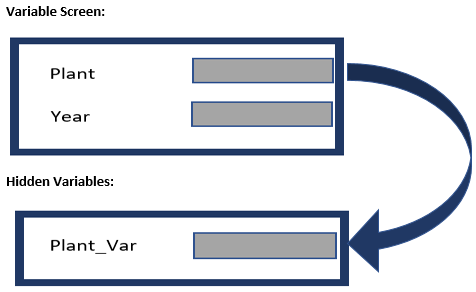
The replacement path processing type needs to be chosen when the value of a variable needs to be automatically replaced on execution of the query. Through the replacement path, we can create hidden variables and later fill them with another variable. For instance, consider a scenario where we have Plant and Year in the variable screen. Plant gets filled from the hidden variable Plant_Var. On the variable screen, you will not see Plant_Var. Based on user selections, the hidden variable is leveraged to collect the proper data from the database as outlined below:
Customer Exit
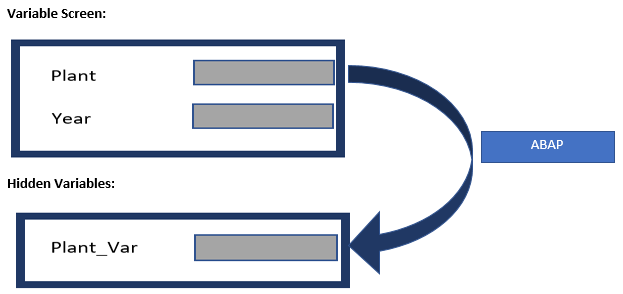
Function module EXIT_SAPLRRS0_001 is leveraged via enhancement RSR00001 when you select the customer exit processing type for a variable. Using this processing type, variables can be filled in the reporting at various points of time, but the code should always be within enhancement RSR00001. This exit primarily functions with hidden variables but can be written with greater complexity than the replacement path processing type. For instance, if you need to join multiple database tables to identify hidden variables, it will require ABAP code to derive the logic. Based on user selections, the custom logic is run to collect the proper data from the database as outlined below:
SAP Exit
Function module RREX_VARIABLE_EXIT is leveraged when the SAP exit processing type is used for a variable. When using this exit, make sure that the variable is filled properly and restrictions are considered in FILL_SP_1.
User Entry/Default Value
If you want an additional screen to pop up for user entry, select this processing type. For example, Sales Organization and Division are available for user entry in the variable selection screen below:
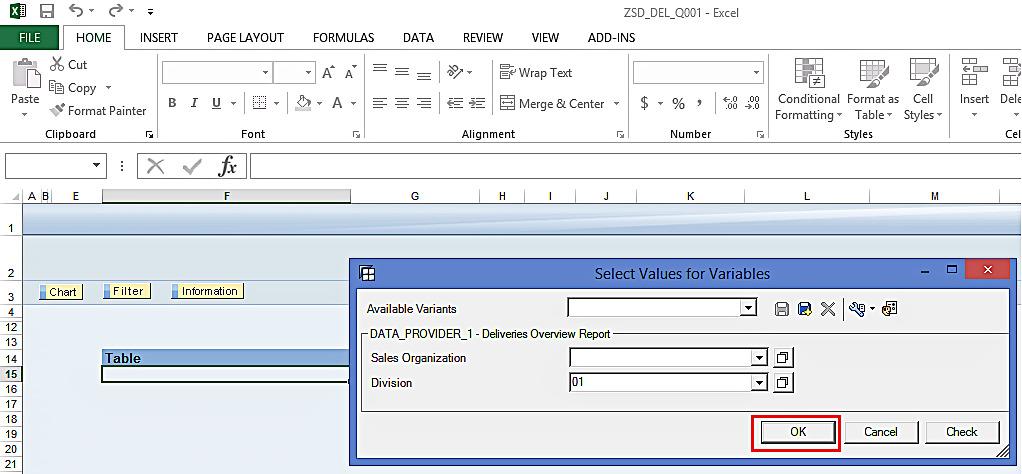
With the user entry processing type, you can specify the variables that will be available for user entry, or you can specify default values based on your requirement. Based on user entry or default values, the proper data is selected from the database.
Authorization
Leverage the authorization processing type if you want to fill the variables automatically based on the authorization of a user. For instance, let’s assume you have a variable screen with Country and Year. The Country variable is derived automatically from the authorizations of the user executing the query.
Applicable Processing Types by Variable Type
Please note that not all variable types can leverage all processing types. There are certain restrictions. Let’s now understand the applicable processing types for each of the different types of SAP BW variables.
CHARACTERISTIC VALUE VARIABLES
Characteristic value variables can have the following processing types:
- User Entry/Default Value
- Replacement Path
- Customer Exit
- SAP Exit
- Authorization
HIERARCHY NODE VARIABLES
Hierarchy node variables can have the following processing types:
- User Entry/Default Value
- Customer Exit
- SAP Exit
- Authorization
TEXT VARIABLES
Text variables can have the following processing types:
- User Entry/Default Value
- Replacement Path
- Customer Exit
- SAP Exit
FORMULA VARIABLES
Formula variables can have the following processing types:
- User Entry/Default Value
- Replacement Path
- Customer Exit
- SAP Exit
HIERARCHY VARIABLES
Hierarchy variables can have the following processing types:
- User Entry/Default Value
- Customer Exit
- SAP Exit
Below is the summary table of the applicable processing types for each of the variable types:
| Variable Type | |||||
| Processing Type | Characteristic Value Variables | Hierarchy Node Variables | Text Variables | Formula Variables | Hierarchy Variables |
| User Entry/Default Value | X | X | X | X | X |
| Replacement Path | X | X | X | ||
| Customer Exit | X | X | X | X | X |
| SAP Exit | X | X | X | X | X |
| Authorization | X | X | |||
—
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP BW tutorials.

No comments:
Post a Comment